Energy efficiency has become a critical aspect of modern facility management, driven by a combination of rising energy costs, environmental concerns, and government regulations. The cost of energy has steadily increased over the years, making it more important than ever to minimize energy waste in facilities. Additionally, with a growing focus on sustainability and reducing greenhouse gas emissions, energy monitoring has become a top priority for organizations.
In facilities, rotating equipment like motors, pumps, and fans typically consume the most energy. By optimizing the energy use of these machines, facilities can significantly reduce energy waste and improve efficiency. This not only lowers energy consumption and carbon emissions, but also increases the reliability and durability of these vital parts.
The efficiency of production processes has a big impact on energy use. By optimizing energy use in these processes, facilities can improve efficiency and reduce costs, leading to increased competitiveness in the market. Many facilities are implementing strategies such as energy-efficient lighting, HVAC systems, and building controls to minimize energy waste and improve efficiency.
Governments around the world have also introduced regulations to promote energy efficiency, further increasing its importance in facilities. These regulations often require facilities to meet specific energy-use targets, making it essential for organizations to monitor and improve energy efficiency to comply with these regulations.
Relationship Between Predictive Maintenance and Energy Efficiency
Impact of Equipment Failures on Energy Consumption
Industrial processes heavily rely on a multitude of interconnected equipment and machinery, each playing a vital role in the overall production cycle. However, when equipment failures occur, they not only disrupt the workflow but also have a profound impact on energy consumption within industrial facilities.
Downtime-Induced Energy Inefficiency:
Equipment failures often lead to unexpected downtime, during which machinery is either completely halted or operates sub-optimally. This downtime results in a considerable loss of energy efficiency, as the systems are idling or running inefficiently without contributing to productive output.
Compromised Operational Parameters:
Faulty equipment may operate outside of optimal parameters, leading to increased energy consumption. For example, a malfunctioning motor may draw more power than necessary, resulting in higher energy costs and a negative environmental impact.
Increased Wear and Tear:
Continuous operation of malfunctioning equipment can exacerbate wear and tear, leading to a higher frequency of breakdowns. This vicious cycle not only contributes to increased maintenance costs but also escalates energy consumption due to inefficient operation.
Early Detection through Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance emerges as a strategic solution to mitigate the impact of equipment failures on energy efficiency. By leveraging advanced monitoring technologies and data analytics, organizations can identify potential issues before they escalate into critical failures.
Correlation between Machine Health and Energy Efficiency
Reduced Energy Consumption in the Manufacturing Sector:
Several manufacturing industries have reported significant reductions in energy consumption after implementing predictive maintenance strategies. Case studies show that identifying and rectifying energy-related equipment failures promptly leads to more efficient operation and lower overall energy costs.
Example: A large-scale automotive manufacturing plant implemented predictive maintenance for its robotic welding systems, leading to a 15% reduction in energy consumption due to timely identification and correction of equipment issues.
Enhanced Efficiency in HVAC Systems:
In facilities where Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems play a crucial role, predictive maintenance has proven to be instrumental in optimizing energy usage. Early detection of issues in HVAC components ensures that the systems operate at peak efficiency.
Example: A commercial building with advanced HVAC predictive maintenance observed a 20% decrease in energy consumption, attributed to the timely replacement of faulty components and optimization of system settings.
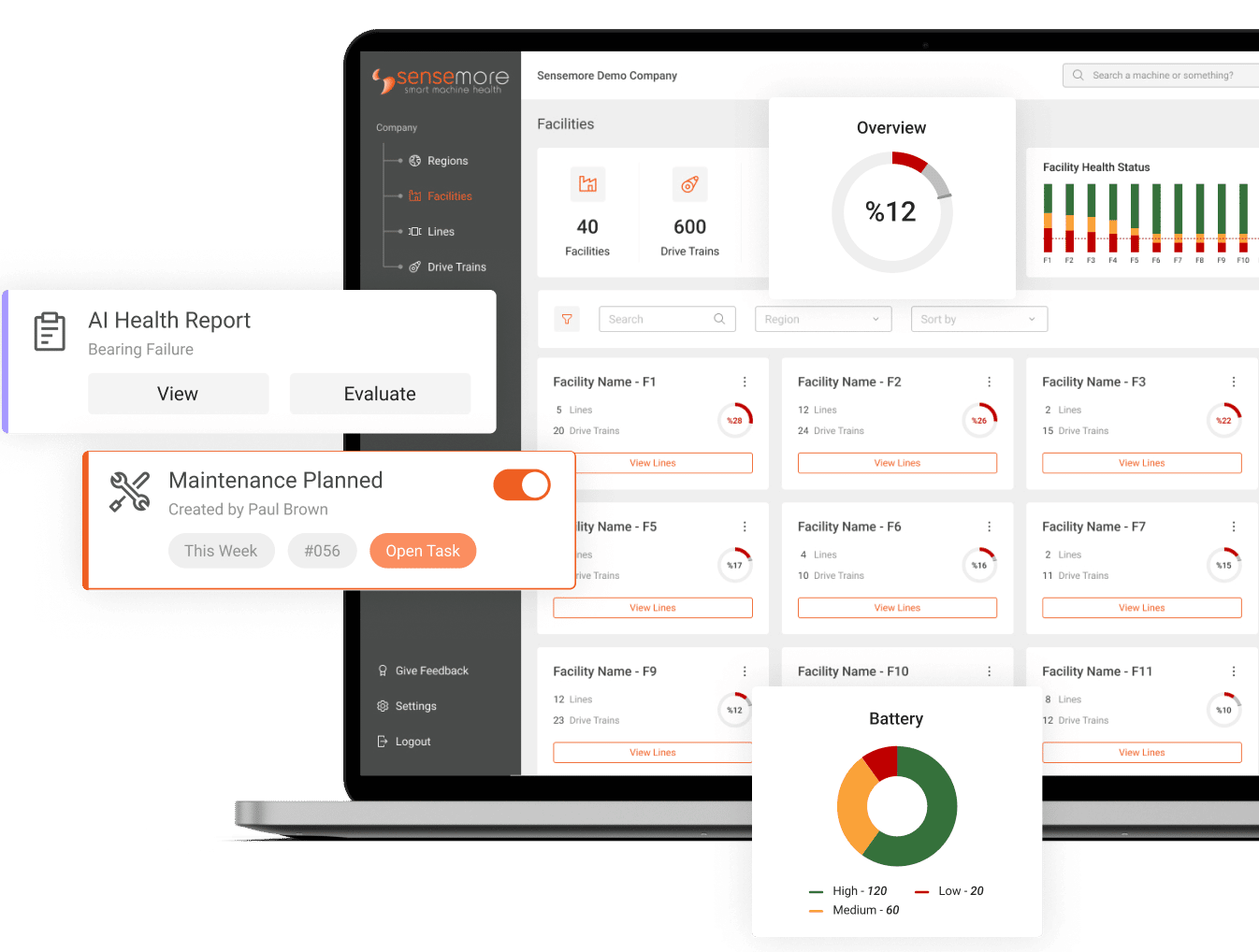
Energy Monitoring Systems
Introduction to Energy Monitoring
Energy monitoring serves as a cornerstone for achieving optimal energy efficiency in industrial applications. Real-time data acquisition involves the continuous collection and analysis of energy-related metrics to provide a dynamic view of energy consumption within a facility.
Smart Metering Systems:
Smart metering technologies play a pivotal role in real-time data acquisition. These devices capture energy consumption data at frequent intervals, allowing organizations to monitor usage patterns, identify peak demand periods, and respond promptly to deviations from expected energy profiles.
Advanced Data Logging Platforms:
Utilizing advanced data logging systems enables the capture of granular data on energy consumption. This data includes information such as voltage levels, current flow, and power factor, providing a comprehensive understanding of how energy is utilized across various processes and equipment.
Integration with SCADA Systems:
Energy monitoring systems often integrate with Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems, facilitating seamless communication between energy data and the industrial control infrastructure. This integration enhances the visibility of energy-related parameters for improved decision-making.
Sensor Technologies and Integration
Sensor technologies play a crucial role in the accurate and detailed monitoring of energy consumption. Various sensors are employed to capture data related to equipment performance, environmental conditions, and overall energy usage.
Power Quality Sensors:
These sensors monitor the quality of electrical power, detecting issues such as voltage fluctuations, harmonics, and power factor. By addressing power quality issues promptly, organizations can prevent equipment damage and enhance overall energy efficiency.
Environmental Sensors:
Monitoring environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity, is essential for understanding their impact on energy consumption. For instance, optimizing HVAC systems based on real-time environmental data contributes to energy savings.
Integration with Industrial IoT Devices:
Energy monitoring systems often leverage the Industrial Internet of Things (IoT) by integrating with a network of connected devices. This interconnected ecosystem allows for comprehensive data collection, enabling a holistic view of energy usage and performance.
Benefits of Integrating Energy Monitoring with Predictive Maintenance
Real-time Anomaly Detection:
Integrating energy monitoring with predictive maintenance enables the continuous monitoring of equipment performance. Real-time anomaly detection identifies deviations from normal operating conditions, allowing for immediate intervention to address potential issues before they impact energy efficiency.
Trend Analysis for Predictive Insights:
Energy monitoring systems facilitate trend analysis by tracking energy consumption patterns over time. This historical data enables predictive maintenance algorithms to identify emerging trends and anticipate future issues, supporting proactive maintenance strategies.
Precision in Energy Consumption Prediction
Data-Driven Predictive Models:
The integration of energy monitoring data enhances the precision of predictive maintenance models. By incorporating real-time energy consumption metrics, predictive algorithms can generate more accurate predictions regarding equipment health and potential failures.
Optimizing Maintenance Schedules:
Energy monitoring contributes to the optimization of maintenance schedules by providing insights into the actual condition of equipment. This allows organizations to prioritize maintenance activities based on real-time energy-related data, reducing unnecessary downtime and associated costs.

Contribution of Energy Monitoring
Energy efficiency and energy monitoring go along with one another. The process of measuring, following, and assessing energy use in a facility is referred to as energy monitoring. On the other hand, energy efficiency refers to minimizing energy waste and optimizing energy utilization within a facility.
Energy monitoring offers a thorough insight of how much energy is utilized in a facility, which may be used to spot inefficient and wasteful energy use. Energy monitoring may give a thorough picture of energy use and assist facilities in finding possibilities to increase energy efficiency by evaluating energy use in real-time.

Energy monitoring is applicable to many different forms of rotating machinery, including motors, pumps, compressors, and other kinds of mechanical machinery. Facilities can identify spots where energy is being wasted, such as equipment that is misaligned, overloaded, or running outside of its ideal range, by monitoring the energy consumption of these components.
Additionally, by keeping an eye on the energy usage of rotating equipment, facilities can see opportunities to enhance the performance of these parts, such as slowing down pumps outside of peak usage times or realigning motors to use less energy. By using energy saving techniques, facilities can increase the energy efficiency of all rotating equipment and minimize energy waste. According to the techniques used, chronic problems can be prevented by determining which equipment or process originates from the energy waste.
To illustrate the impact of energy monitoring on maintenance costs with an example, compressed air leaks are an important source of wasted energy in air systems in industry. 25-30% of the compressed air at the compressor outlet is wasted due to leaks on the line. In a well-maintained system, the percentage lost due to leakage should be less than 10%.
The operating cost of an air compressor is more than the initial purchase. Industrial air compressors consume a lot of energy. When they are not working as efficiently as they should, some of this energy use does not contribute to the operation of the facility. If 170 m3/h of air is needed and the leakage level stays at 30%, 220 m3/h of air must be produced to compensate.
For reference, an air compressor consumes an average of 20 kW of energy per 170 m3/h. Therefore, producing 50 m3/h more to compensate for the air loss increases the energy cost by about 30%. The Compressed Air and Gas Institute (CAGI) estimates that a 6mm leak could cost you $2,500 to $8,000 per year. While the increase in energy consumption in the compressors can be monitored by energy monitoring, on the other hand, it allows root-cause analysis to be made on the side of whether the increase in energy consumption from the current and voltage signals used in energy monitoring is due to gas leakage in the line or a fault on the machine.
Promoting Sustainability
Sustainability may be greatly aided by energy monitoring in the industrial sector, especially for rotating machinery. Energy monitoring offers useful information on energy use, which may be used to execute energy-saving measures that both directly and indirectly lower carbon emissions related to energy production.

Energy monitoring can also encourage the industrial sector to embrace green technology. Facilities can evaluate the effectiveness of various energy-saving measures and decide which technologies to install to further increase energy efficiency by monitoring energy use over time. This can involve implementing energy-saving technology, such as energy recovery systems.
By offering data-driven insights into energy use, energy monitoring of rotating equipment in the industrial sector may assist facilities in achieving their sustainability goals. Facilities may effectively promote sustainability by reducing carbon emissions, financial and environmental costs of energy by putting energy-saving measures into place and utilizing green technology.
Application of Energy Monitoring
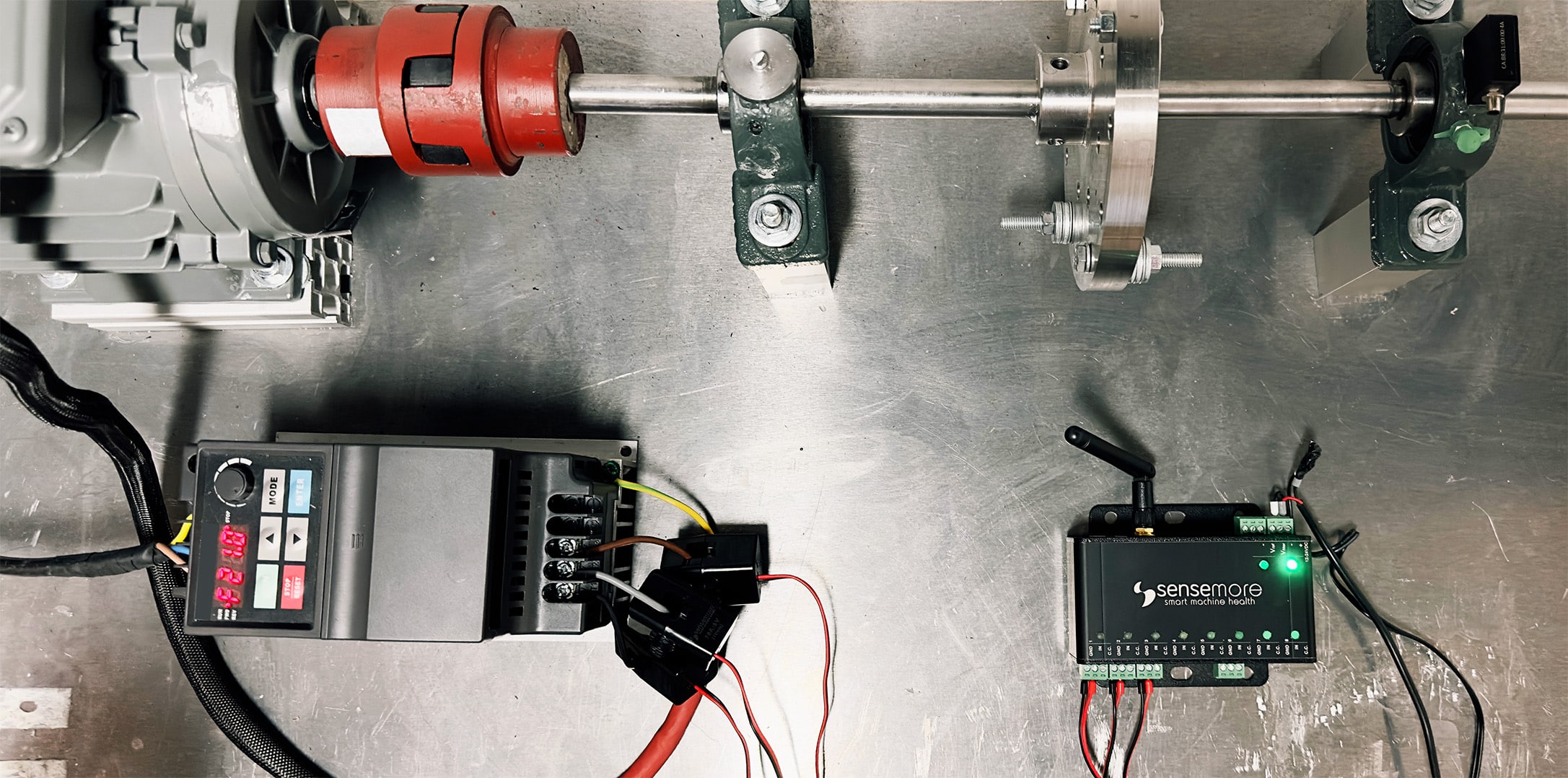
Sensemore performs energy monitoring applications by calculating the power consumed by motors driving rotating equipment. For power calculations, current and voltage information from the phase cables feeding the motor is taken through analog sensors. Since the collected analog data includes the phase difference information between voltage and current, the power factor is also calculated. The collected data is transferred to the cloud with the analog data collection device Duck, and power and energy consumption are calculated. Data collected and calculated on the cloud application is displayed. Point-based and total energy consumptions are displayed and inefficient points on the line are detected as well as the anomalies resulting in irregular current and voltages in the input cables of the motors with their root causes.
Recommended Blog Posts
September 4, 2023
Powerful Signal Analysis Tools for Vibration Analysis
Predictive maintenance, crucial for machinery reliability, heavily relies on vibration analysis. Techniques like FFT…
September 4, 2023
Rotating Machinery Vibration Analysis
Vibration analysis is a critical tool in various industries like manufacturing, power generation, and transportation.…
December 28, 2022
Fault Diagnostic Technique Using Machine Mode Similarity Analysis
AI can diagnose machine faults with vibration data but machine mode similarity analysis is an alternative, it uses…
September 15, 2022
Understanding Rotating Machinery Data
Machine data is generated by physical attributes and actions of machines, collected by sensors and analyzed for…
August 6, 2021
Envelope Analysis
Bearings are critical elements in rotating machines, they support radial and axial loads, and reduce friction. Real…
May 6, 2021
What is Cepstral Analysis?
Cepstral Analysis, a tool used to detect periodicity in frequency spectrum, can be useful in gearbox fault detection in…
October 9, 2020
How is Fault Detection Performed?
Vibration measurements and analysis, using multiple parameters, can identify developing problems in machinery before…
September 21, 2020
Parameter Selections in Vibration Measurement
Vibration measurements are used to determine the response of machines to forces and identify potential issues. It is…
September 4, 2020
What is Vibration Analysis?
Vibration analysis can be used to discover problems in machines and predict when they might fail. It can significantly…
Sensemore Energy Monitoring Solution
If you enjoyed this blog, explore our Energy Monitoring Solution page.