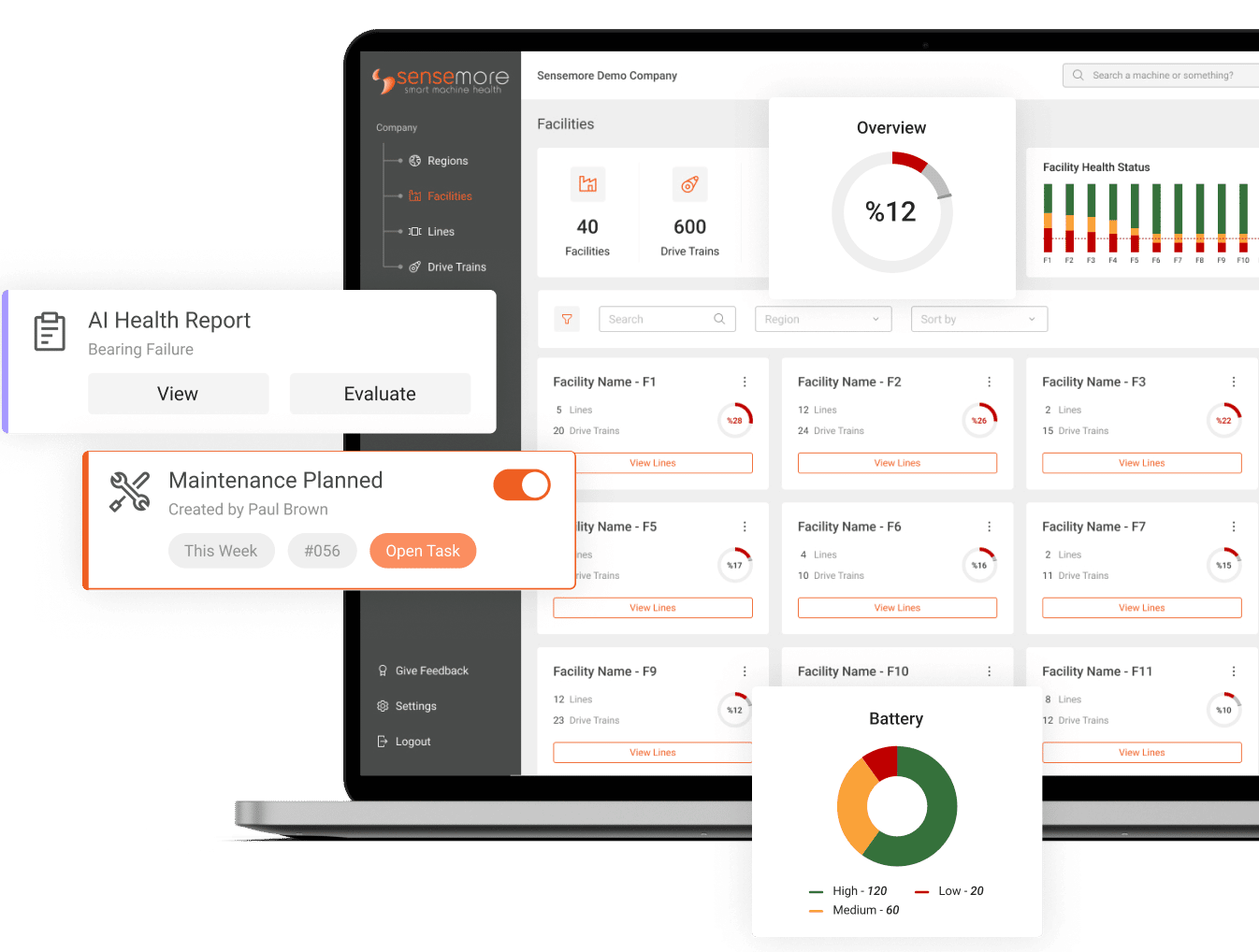
Maintenance is a comprehensive concept encompassing tests, measurements, replacements, adjustments, and repairs aimed at enhancing overall system health. This blog explores the future of maintenance cultures. In the early stages, Corrective Maintenance prevailed, addressing malfunctions reactively as they occurred. Pre-industrial revolution systems lacked condition monitoring, making this approach viable at the time. But, future of maintenance is much more progressive.
The Industrial Revolution elevated maintenance’s importance, particularly with safety concerns in equipment like boilers. This led to the adoption of Preventive Maintenance, focusing on periodic processes to prevent malfunctions. As demand grew, this approach expanded beyond boilers to various machinery in diverse plants.
Post-World War 2, Proactive Maintenance emerged, emphasizing reliability and system availability. Utilizing fault analysis and condition monitoring, this approach allows for evaluating failures, conducting criticality analysis, and taking preemptive action before malfunctions occur. This evolution showcases how maintenance practices have adapted to technological advancements and market demands throughout history.
Embracing a forward-looking approach, predictive maintenance has revolutionized how systems are managed and sustained. Predictive maintenance represents a shift from reactive to proactive strategies. By harnessing advanced technologies, it anticipates and addresses potential issues before they manifest, optimizing system reliability.
Key Technological Advancements
Development of Sensors and IoT:
The advent of sensors and the Internet of Things (IoT) has been instrumental in predictive maintenance. Real-time data collection from equipment provides insights into performance, enabling timely intervention before failures occur.
Integration of Big Data Analytics:
Big Data analytics has empowered predictive maintenance by processing vast amounts of data. Analyzing patterns and trends allows for more accurate predictions and targeted preventive actions, reducing downtime and enhancing efficiency.
Current State of Maintenance Culture
Maintenance culture stands at the intersection of tradition and innovation, with technology playing a pivotal role in shaping contemporary practices.
Role of Technology in Shaping Maintenance Practices
The integration of cutting-edge technologies has redefined maintenance strategies. From advanced sensors for real-time monitoring to sophisticated analytics platforms, technology enhances predictive capabilities, reduces downtime, and extends the lifespan of critical systems.
Industry Adoption Rates and Trends
Across diverse industries, the adoption of modern maintenance practices varies. Some sectors have swiftly embraced the digital transformation of maintenance, while others are still navigating the transition. Trends indicate a growing recognition of the cost-effectiveness and operational benefits associated with technology-driven maintenance.
Future of Maintenance Culture
Anticipating the future of maintenance culture involves a dynamic interplay of emerging technologies poised to reshape traditional practices.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Maintenance
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) algorithms anticipates, analyzes, and optimizes maintenance processes. AI-driven systems learn from historical data, predict potential issues, and recommend proactive measures, fostering a more intelligent and responsive future of maintenance culture.
Robotics and Automation in Maintenance Processes
Robotics and automation are set to redefine the hands-on aspects of maintenance. Autonomous robots equipped with maintenance capabilities can perform routine tasks, inspections, and even repairs in challenging environments, improving efficiency and safety.
Integration of Augmented Reality in Maintenance Training
Augmented Reality (AR) is poised to revolutionize maintenance training by providing immersive and interactive experiences. Technicians can access real-time information, visual guides, and remote expert assistance through AR interfaces, enhancing training efficiency and skill development.
Cultural Shifts and Human Factors
The significance of cultural shifts and human factors cannot be overstated. These elements are integral to the successful integration and sustainability of advanced maintenance practices.
Changing Mindset Towards Maintenance
A fundamental aspect of the ongoing transformation in maintenance culture is the evolving mindset towards maintenance itself. Historically viewed as a reactive necessity, there is a paradigm shift towards proactive, preventive, and predictive approaches. This changing mindset emphasizes the strategic role of maintenance in enhancing overall system reliability, reducing downtime, and optimizing resource utilization. Encouraging a mindset that anticipates and addresses issues before they escalate is pivotal in fostering a culture of continuous improvement and efficiency.
Importance of Training and Skill Development
As maintenance practices evolve, the need for continuous training and skill development becomes paramount. The integration of advanced technologies such as predictive maintenance, AI, and robotics necessitates a skilled workforce capable of navigating these innovations. Training programs should not only focus on technical proficiency but also on fostering a deep understanding of the underlying principles driving modern maintenance. Investing in the professional development of maintenance personnel ensures that they can effectively leverage new technologies, interpret data accurately, and contribute to the overall success of the maintenance strategy.
Organizational Culture and Maintenance Excellence
The cultural fabric of an organization plays a central role in achieving maintenance excellence. A culture that values and prioritizes maintenance as a strategic function tends to be more adaptable to change and innovation. Communication channels that facilitate collaboration between maintenance teams, management, and other departments contribute to a holistic approach to maintenance. Additionally, an organizational culture that encourages a proactive rather than reactive approach to challenges fosters an environment where maintenance excellence can thrive. Recognizing and rewarding maintenance achievements further reinforces a culture that values continuous improvement and excellence in maintenance practices.
Recommended Blog Posts
September 4, 2023
Powerful Signal Analysis Tools for Vibration Analysis
Predictive maintenance, crucial for machinery reliability, heavily relies on vibration analysis. Techniques like FFT…
September 4, 2023
Rotating Machinery Vibration Analysis
Vibration analysis is a critical tool in various industries like manufacturing, power generation, and transportation.…
December 28, 2022
Fault Diagnostic Technique Using Machine Mode Similarity Analysis
AI can diagnose machine faults with vibration data but machine mode similarity analysis is an alternative, it uses…
September 15, 2022
Understanding Rotating Machinery Data
Machine data is generated by physical attributes and actions of machines, collected by sensors and analyzed for…
August 6, 2021
Envelope Analysis
Bearings are critical elements in rotating machines, they support radial and axial loads, and reduce friction. Real…
May 6, 2021
What is Cepstral Analysis?
Cepstral Analysis, a tool used to detect periodicity in frequency spectrum, can be useful in gearbox fault detection in…
October 9, 2020
How is Fault Detection Performed?
Vibration measurements and analysis, using multiple parameters, can identify developing problems in machinery before…
September 21, 2020
Parameter Selections in Vibration Measurement
Vibration measurements are used to determine the response of machines to forces and identify potential issues. It is…
September 4, 2020
What is Vibration Analysis?
Vibration analysis can be used to discover problems in machines and predict when they might fail. It can significantly…